OVER WHEELS Device

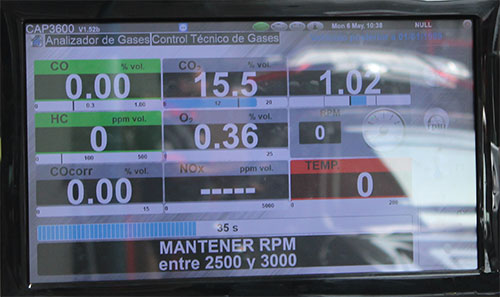
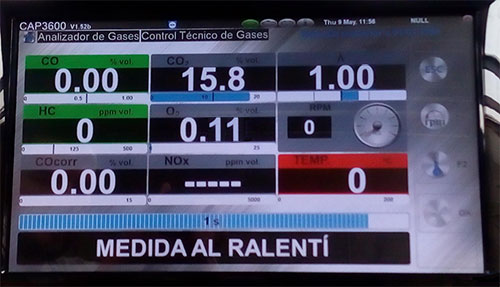
After OVER WHEELS implementation : Test at 2500 RPM and Test at Idle
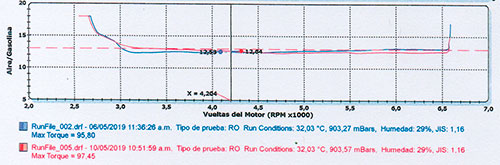
Dynamometer Test ( PAR ): Toyota Yaris 2018
The Toyota Yaris (2018) underwent a dynamometer test to evaluate the performance impact of the OVER WHEELS device. The test results clearly demonstrate the improvement in torque and fuel mixture efficiency after installation.
- Test Details:
- RPM range: up to 4,204
- Blue line: results before OVER WHEELS installation
- Red line: results after OVER WHEELS installation
The results show that, with the device installed, the vehicle achieves an optimal LAMBDA value, ensuring a more precise fuel-air mixture and improved combustion efficiency.
- Before installation (Blue line): 95.34 lb-ft
- After installation (Red line): 97.44 lb-ft
This demonstrates a gain of 3 lb-ft in torque, reflecting improved engine efficiency and performance. The test confirms that OVER WHEELS enhances power delivery while optimizing fuel consumption.
Click on the images to see enlarged versions and appreciate the difference between before and after installation.
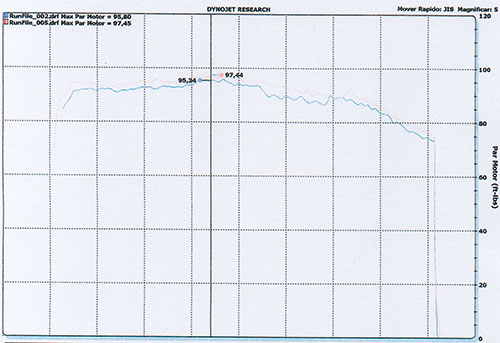
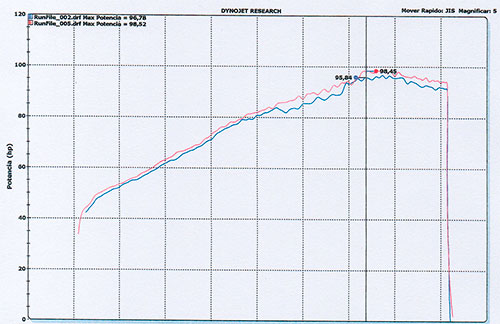
Dynamometer Test: Power Output – Toyota Yaris 2018
 The Toyota Yaris (2018) underwent a dynamometer test to evaluate the power improvements achieved with the installation of the OVER WHEELS device. The test clearly demonstrates enhanced performance and improved fuel mixture efficiency.
The Toyota Yaris (2018) underwent a dynamometer test to evaluate the power improvements achieved with the installation of the OVER WHEELS device. The test clearly demonstrates enhanced performance and improved fuel mixture efficiency.
Test Details:
- RPM range: up to 5,687
- Blue line: results before OVER WHEELS installation
- Red line: results after OVER WHEELS installation
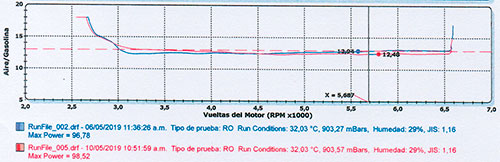
The results show that the device helps the vehicle maintain an optimal LAMBDA value, ensuring a better fuel-air mixture and more efficient combustion.
Power Results:
- Before installation (Blue line): 95.84 units of power
- After installation (Red line): 98.84 units of power
This demonstrates a gain of 3 units of power, confirming that OVER WHEELS enhances engine output while optimizing fuel consumption.
Click on the images to view enlarged versions and clearly observe the difference between before and after installation.
Important considerations to keep in mind:
- Kilowatts (kW): This is the standard unit for the power of an electric motor. It refers to the rate at which the motor generates or consumes power.
- Horsepower (hp): This is another common unit of power. It can be converted from kilowatts by multiplying by approximately 1.34 (1 kW ≈ 1.34 hp).
- Motor Power Calculation: The power of an electric motor can also be calculated by multiplying the voltage by the current (P = V × I) to obtain watts, and then converting to kilowatts.
- What is it?: It measures how many miles a vehicle can travel with one kilowatt-hour of battery energy.
- How is it calculated?: Divide the vehicle's total range in miles by its battery capacity in kilowatt-hours (kWh).
- Example: A vehicle with a range of 280 miles and a 77 kWh battery has an efficiency of approximately 3.6 mi/kWh (280 div 77 ≈ 3.6).
- Performance indicator: A higher mi/kWh figure indicates a more efficient vehicle.
|
Parameter |
Value | Unit |
| Average Gas Consumption | 10.9 | KM / L |
| Gasoline consumed volume | 1.1 | Km |
| Distance traveled | 12.0 | Km |
After
|
Parameter |
Value | Unit |
| Average Gas Consumption | 14.4 | KM / L |
| Gasoline consumed volume | 0.7 | Km |
| Distance traveled | 12.0 | Km |
Photos of the installation of the device, before and after OVER WHEELS: (click on the images to see them enlarged)
(Read more , Tests and Results)